
| +420 549 495 952 |
| hofr@lablifeb.com |
| Building A2/1.16 Kamenice 753/5 625 00 Bohunice - Brno |
Publications
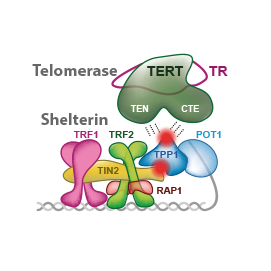
In this review, we summarize quantitative assessments and structural information describing human shelterin and telomerase along with the status of the most promising approaches to telomerase inhibition in cancer cells. We focus on how shelterin allows telomerase action. We evaluate how the identified critical interactions of telomerase and shelterin might be elucidated in future research of new anticancer strategies.
We review:
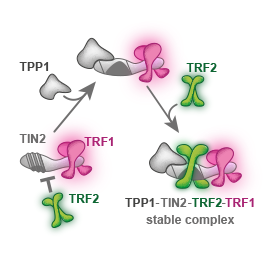
We showed that telomeric repeat binding factor TRF1 can replace TRF2 on TIN2. We described the role of TPP1 as a mediator of the shelterin core assembly at the single-molecule level.
Highlights:
We propose a molecular mechanism that interprets why TPP1 is essential for the stable formation of TRF1–TIN2–TRF2 core shelterin complex.
Download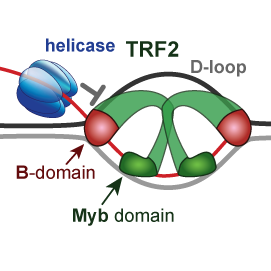
We explain how telomeric proteins TRF2 and RAP1 modify BLM helicase activity and processing of displacement loop (D-loop) during replication of telomeres. We addressed the role of the basic domain (B-domain) of TRF2 in the stabilization of DNA loops.
Highlights:
We suggested a mechanism for how the B-domain stabilizes D-loop and how RAP1 reverts the stabilization.
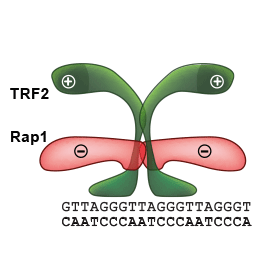
Our quantitative functional studies explain how telomeric proteins cooperate in order to selectively recognize human telomeric DNA. We investigated human Rap1–TRF2–DNA interactions by quantitative approaches. Our findings could be applied on all proteins that recognize DNA selectively and preserve genome stability.
Highlights:
We suggested a possible mechanism of how Rap1 affects the recognition of telomeric DNA by TRF2
Download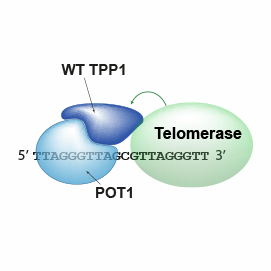
These quantitative observations describe how the TEL-patch part of telomeric protein TPP1 stabilizes telomerase on telomeric DNA and explains its contributions to telomerase recruitment and action.
Highlights:
© 2026, Life B Webdesign: Lukáš Hladecek